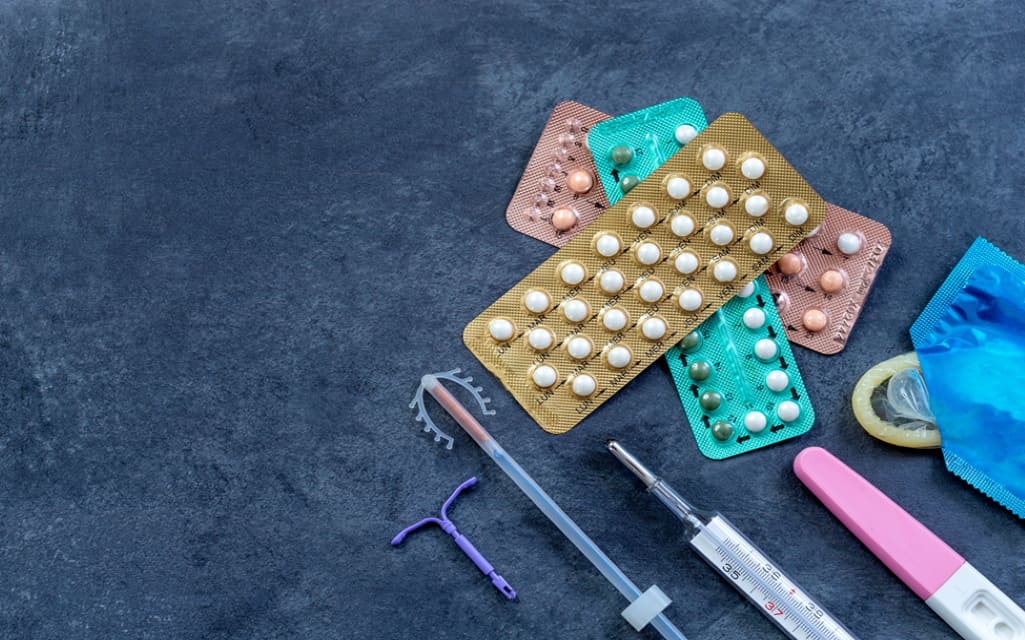
Unexpected pregnancies are far from uncommon in the United States.
Indeed, an incredible 45% of all pregnancies fit this description every year. That’s almost 1 in 2 that are unplanned by the soon-to-be parents.
For some people, of course, an unplanned pregnancy is still a cause for celebration!
For many others, though, it’s a troubling time that’s fraught with big stress, anxiety, and uncertainty at what’s to come. The life-changing nature of having a baby makes birth control an important issue.
Anybody who doesn’t feel ready for parenthood should know about the types of birth control available. After all, in order to avoid any baby-shaped surprises, it’s important to be pro-active with the requisite precautions.
Knowing your options is the first step to doing exactly that. Sound good?
Read on to learn all about 7 of the most effective forms of birth control available.
1. Avoiding Sexual Intercourse!
We say this with our tongue held firmly in our cheeks.
It’s unlikely to be the first form of contraception you had in mind! However, it’s important to note that the most effective form of birth control is not having penetrative sex in the first place.
Be aware that no other available contraception on this list is 100% effective.
There’s always a chance, however slight, that sperm will meet the egg and a baby will be made. Unless that is, you avoid having sex altogether. Of course, that’s unlikely, and we don’t say it to scare you out of intimacy with your partner.
Engaging in sexual intercourse is a natural part of a healthy relationship. It’s just a fact of life that it can end up with pregnancy, regardless of any other precautions you take.
2. Sterilization
The ‘next best thing’ as it were, is permanent birth control (otherwise referred to as sterilization).
Both men and women can choose to be made sterile via particular surgical procedures.
Men can get a vasectomy, which is where the tubes in their testes are cut and sealed. This prevents sperm from entering the semen.
Women can opt for what’s called a tubal ligation. You might have heard this referred to in its colloquial phrasing, ‘getting your tubes tied’. Here, the fallopian tubes are sealed, cut, tied, or otherwise blocked.
Both are one-time, permanent procedures. Again, though, even sterilization procedures aren’t 100% effective. Expect a 1% chance of getting pregnant post-surgery.
3. The Pill
The pill is a particularly common hormonal contraception.
Taken by women, a specific hormone called progestin is released into their system that prevents ovulation. The lack of ovulation means eggs aren’t around to be fertilized by the sperm.
At the same time, the influx of hormones fosters the development of mucus in the cervix. This works to make the journey to the uterus far more difficult for sperm as well.
Altogether, pregnancy is avoided 99% of the time.
Be aware that taking the pill is a daily commitment. Forgetting to take them, or taking them at different times of day, will decrease their effectiveness.
Always learn more about any contraceptive medication before taking it, and speak to a doctor to fully understand the repercussions.
4. Condoms
Condoms are arguably the most well-known of all the prevailing contraceptives.
Unfortunately, they’re also less effective, protecting against unplanned pregnancies 98% of the time. Note that this applies even when the condoms are used correctly. The chance of pregnancy increases when mistakes are made in their application.
These latex (or polyurethane) sheathes are fitted over the guy’s erect penis. In so doing, sperm that’s released during intercourse is prevented from entering the vagina.
An added bonus of condoms is how they facilitate sexual health as well. There’s less chance of both pregnancy and passing on/contracting sexually transmitted diseases.
So-called femidoms, or female condoms, are also available. These are placed in the vagina as opposed to over the penis, but help protect against pregnancy (95% of the time) in the same way.
5. IUD
This is another effective contraceptive that works in both hormonal and non-hormonal forms. They’re effective 99% of the time and can function for years without needing replacement.
A health care professional inserts a tiny, ‘t-shaped’ device (the IUD) into a woman’s uterus.
The hormonal version of the IUD is plastic and releases progestin (the same hormone released via the aforementioned pill) into their system. The non-hormonal version is made of copper and prevents sperm from reaching the egg.
Whenever you feel ready for a baby, simply have the IUD removed and get to work! In the meantime (among other potential issues) there’s a chance of cramps, irregular periods, and (in rare cases) the IUD getting stuck in the uterus.
6. The Implant/Rod
Another 99% effective birth control method, the implant is a matchstick-sized, rod-like device that’s inserted via injection into a woman’s arm or hip.
It goes without saying that a healthcare professional needs to do the insertion itself!
The implant works in the same way as the pill and plastic IUD, by releasing the hormone progestin. In so doing, ovulation is prevented, which stops eggs from being released by the ovaries. At the same time, the mucus lining the cervix will thicken and make it harder for sperm to enter the uterus.
The implant lasts for around 3 years before it will need replacing.
7. The Shot/Depo Provera
This form is birth control is similar to the implant. However, rather than a progestin-releasing rod being inserted into your body, a woman gets a single shot of the hormone instead.
The shot itself is often referred to as Depo Provera.
The progestin works to prevent pregnancy in exactly the same, via ovulation privation and thickening of cervical mucus. Its effectiveness against pregnancy is the same too, at around 99%.
Among others, the downsides include discomfort, headaches, and the need to have the shot again at the same time, 3 months later. Health complications can also arise with continued use after 2 years.
The Top Types of Birth Control
Millions of people experience the shock of an unplanned pregnancy each year.
To prevent that eventuality it’s important to know about the types of birth control and find the right option for you. Hopefully, this post has revealed a top selection of options to try.
Looking for more articles like this one? Search ‘pregnancy’ on the website now.