In the digital age, where every online interaction can significantly impact brand visibility and search rankings, understanding the backbone of SEO is more crucial than ever. One such backbone, often overlooked yet profoundly influential, is the use of meta tags. Designed to provide search engines with information about a webpage, these snippets of text play a pivotal role in SEO strategies. This guide is tailored for digital marketers and content creators eager to harness the power of meta tags to boost their online presence.
What are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are pieces of HTML code that reside in the header of a web page. They don’t appear on the page itself, but they provide valuable data about the page to search engines and developers. Think of them as the “behind-the-scenes” information conveying the content’s essence, thereby guiding search engine crawlers through a webpage’s context and content priorities.
Why Meta Tags Are Important for SEO
The importance of meta tags in search engine optimization is immensely crucial and should not be underestimated. They directly influence click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs) by offering a preview of the page content. Well-crafted meta tags can attract visitors, while poorly executed ones can deter potential traffic. In essence, meta tags serve as both a billboard and a compass — enticing users while guiding search engines.
The 11 Most Important Meta Tags You Need to Know
Below is an overview of the ten critical meta tags that are indispensable for SEO optimization:
Title Tag
The Title Tag stands as perhaps the most essential meta tag for search engine optimization. It is the first line that users see on a search engine results page (SERP) and significantly influences whether they click on a link. The title tag should concisely and accurately describe the page’s content while incorporating relevant keywords to improve search rankings.
Best Practice:
- Length: Keep your title tag between 50-60 characters to ensure it displays fully on SERPs without getting cut off.
- Keyword Placement: Place important keywords towards the beginning of the title tag to catch both the user’s and the search engine’s attention early.
- Brand Name: If space permits, include your brand name at the end of the title tag for recognition. However, the focus should remain on including relevant keywords that accurately describe the content.
Example:
Suppose you have a webpage about homemade Italian cooking. A well-crafted title tag might look like this:
`Homemade Italian Pasta Recipes – Delicious and Easy | Gino’s Kitchen`
In this example, the primary keyword “Homemade Italian Pasta Recipes” is placed at the beginning to improve visibility and search relevance. The addition of “Delicious and Easy” provides a value proposition to the reader, indicating what they can expect to find on the page. Including the brand name “Gino’s Kitchen” at the end helps with brand recognition without sacrificing the importance of the keywords.
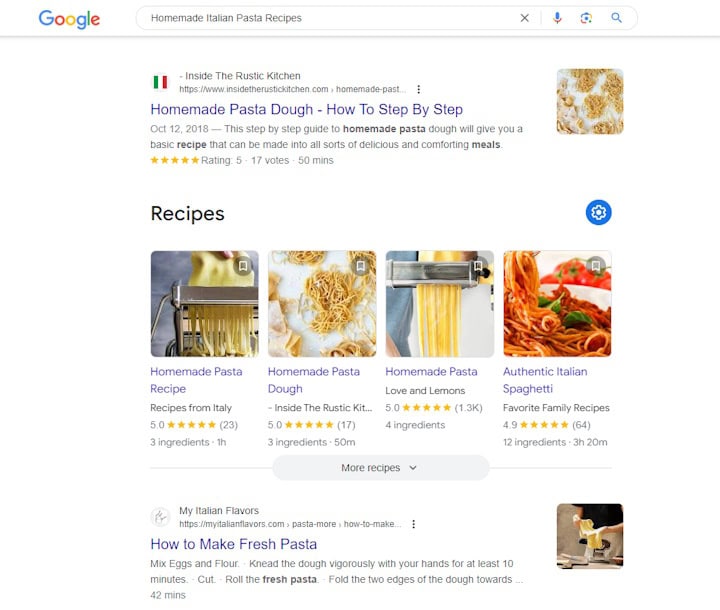
Crafting an effective title tag is both an art and a science, requiring a balance between being appealing to users and optimized for search engines. Always keep the user intent in mind and strive to offer clear and enticing reasons to click through to your webpage.
Related: 14 Best Link Building Services You Should Consider
Meta Description
The Meta Description tag provides a brief summary of a webpage’s content, typically displayed under the title tag on SERPs. While it does not directly impact search rankings, a well-written meta description can increase click-through rates and improve user experience by setting expectations for what users will find on the page.
Best Practice:
- Length: Keep your meta description between 150-160 characters to ensure it displays fully on SERPs without getting cut off.
- Value Proposition: Use this tag as an opportunity to entice users by highlighting the page’s benefits or unique features.
- Call-to-Action (CTA): End your meta description with a CTA that encourages users to click through to your webpage.
Example:
Using the previous example, a compelling meta description for the homemade Italian cooking page could be:
`Easy Homemade Italian Pasta Recipes at Gino’s Kitchen. Impress your family and friends with authentic flavors. Try them now!`
<meta name="description" content="Easy Homemade Italian Pasta Recipes at Gino's Kitchen. Impress your family and friends with authentic flavors. Try them now!"/>In this example, the value proposition of “delicious and easy” is reinforced from the title tag, while the CTA “try them now” encourages users to click through and try the recipes for themselves.
Canonical Tag
The Canonical Tag helps to avoid duplicate content issues by informing search engines which version of a web page is the preferred one. When multiple URLs have similar or identical content, using canonical tags can prevent search engines from penalizing your website for duplicate content.
Best Practice:
- Consistency: Be consistent with using canonical tags to avoid confusion and ensure the correct version of a page is indexed by search engines.
- URL Structure: Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred URL structure, especially when using different variations (e.g., HTTP vs. HTTPS).
`<head>`
`<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/homemade-italian-pasta-recipes">`
`</head>`Example:
Suppose you have multiple pages with similar content, such as a page for “Homemade Italian Pasta Recipes” and another for “Easy Homemade Pasta Recipes.” In this case, you can use a canonical tag to specify which one is the preferred version, avoiding duplicate content issues.
Header Tags
Header tags (H1-H6) are HTML elements that indicate the heading or subheadings on a webpage. These tags help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your content, making it easier to index and rank.
Best Practice:
- Hierarchy: Use header tags in a hierarchical order (H1 followed by H2, H3, etc.) to indicate the importance and relationship between different sections of your content.
- Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords in your header tags, but avoid keyword stuffing or making them overly long.
Example:
For the homemade Italian cooking page, the title of the recipe could be an H1 tag, followed by subheadings for ingredients (H2), instructions (H3), and variations (H4).
Related: Why Is My Homepage Indexed But My Posts Aren’t Ranking?
Image Alt Tags
Image Alt Tags provide alternative text for images, allowing search engines to understand the image’s context. Since search engine crawlers cannot “see” images, alt tags help them determine what the picture is about and index it accordingly.
Best Practice:
- Relevance: Use descriptive keywords that accurately describe the image’s content.
- Conciseness: Keep your alt tags short and to the point. Avoid using long sentences or paragraphs.
Example:
For an image of a delicious bowl of homemade Italian pasta, the alt tag could be “Homemade Italian Pasta Recipe with Fresh Tomato Sauce.” This alt tag accurately describes the image and incorporates relevant keywords.
Schema Markup
Schema Markup is a form of structured data that can be added to your webpage’s HTML code to help search engines understand the content better. It provides additional information about the webpage, such as its type, author, date published, and more.
Best Practice:
- Relevance: Use relevant schema markup for your content type (e.g., recipes, articles, events, etc.).
- Accuracy: Make sure the schema markup accurately reflects the content on your webpage to avoid confusion and potential penalties from search engines.
Example:
For the recipe page on homemade Italian cooking, you could use Recipe Schema Markup to provide additional information about the dish, such as ingredients, cook time, and nutrition facts. This can help search engines display rich snippets in their results, providing users with more information and increasing click-through rates.
Here how should Schema Markup looks like:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Recipe",
"name": "Homemade Italian Pasta Recipe with Fresh Tomato Sauce",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Gino's Kitchen"
},
"datePublished":Open Graph Tags
Open Graph Tags are HTML meta tags used to enhance the content’s appearance when shared on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. They allow you to control how your webpage is presented in social media feeds, making it more visually appealing and encouraging users to click through.
Best Practice:
- Consistency: Use consistent branding across all open graph tags to maintain a cohesive look and feel for your content.
- Image Optimization: Use high-quality and optimized images in your open graph tags to attract attention and increase click-through rates.
Example:
For the homemade Italian cooking page, you could use Open Graph Tags to display an enticing image of the dish, along with a catchy headline and brief description. This can help grab users’ attention and entice them to click through to your webpage.
The main Open Graph tags:
<meta property="og:title" content="Homemade Italian Pasta Recipes">
<meta property="og:description" content="Impress your family and friends with delicious and authentic homemade Italian pasta recipes.">
<meta property="og:image" content="[image URL]">Robots Meta Tag
The Robots Meta Tag allows you to specify instructions for search engine crawlers on how to crawl and index your webpage. This tag can be used to prevent certain pages from being indexed or to specify the priority of specific pages.
Best Practice:
- Relevancy: Use robots meta tags only when necessary, such as for pages that contain sensitive information or duplicate content.
- Accuracy: Make sure the instructions provided in the robots meta tag align with your website’s overall SEO strategy.
Example:
For the homemade Italian cooking page, you may want to prevent search engines from indexing certain images or video content. In this case, you can use a robots meta tag with the “noindex” instruction for those specific elements. This will ensure they are not indexed and do not affect your website’s overall SEO performance.
Nofollow Attributes
Nofollow attributes are HTML attributes that tell search engines not to follow or credit links on a webpage. This can be helpful for preventing the transfer of link equity to untrustworthy or irrelevant websites, such as spammy comment sections.
Best Practice:
- Relevance: Use nofollow attributes for external links that you do not want to give credit to or that may not be relevant to your content.
- Accuracy: Make sure the nofollow attribute is only used when necessary and does not affect internal links or other essential pages on your website.
Example:
For the homemade Italian cooking page, you may have a section with recommended kitchen tools. In this case, you could use a nofollow attribute for these external affiliate links to avoid giving them link equity and potentially harming your website’s SEO.
HTML standard tags
HTML standard tags are basic HTML elements that define the structure of a webpage. They provide important information to search engines and web browsers about how to display the content.
Best Practice:
- Consistency: Use standard tags consistently throughout your content for better readability and consistency in code.
- Accessibility: Make sure your content is accessible by using proper HTML tags, such as heading tags for titles and subheadings for sections.
Example of HTML standard tags :
For the homemade Italian cooking page, you could use <h1> tags for the title of the recipe, <h2> this tags for ingredient lists, and <p> tags for instructions. This will not only make your content more organized and easier to read but also provide important information to search engines about the hierarchy and structure of your webpage’s content.
<h1> <h2> <h3>: These are heading tags used to define the main title and subheadings of a webpage.
<p>: This is a paragraph tag used for general text content.
<strong>: This is a strong tag used to emphasize or highlight important text.
<ul>, <ol>, <li>: These are list tags used to create bullet or numbered lists.
<table>: This is a table tag used to organize data in rows and columns.
<form>: This is a form tag used for user input, such as filling out a contact form.
<img>: This is an image tag used to display images on a webpage.
<a>: This is an anchor tag used to create clickable links to other webpages.Viewport tag
The Meta Viewport Tag is a necessary tag for responsive web design. It allows you to control how the webpage is displayed on different devices, such as desktops, tablets, and mobile phones.
Best Practice:
- Responsiveness: Make sure your website is optimized for different screen sizes by using the meta view port tag.
- Consistency: Test your webpage on different devices to ensure the content is displayed correctly and consistently.
Example:
For the homemade Italian cooking page, you could use the meta view port tag to specify the width and scale of the webpage for mobile devices. This will ensure that users can easily navigate and read your content on their phones without any issues.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
The “width=device-width” part sets the width of the page to follow the screen’s width on different devices. The “initial-scale=1.0” part sets the initial zoom level when the webpage is first loaded on a device.
How to Optimize Meta Tags for Better SEO
Optimizing meta tags involves balancing relevance and keyword inclusion without over-optimization or keyword stuffing. Here are succinct guidelines:
- Ensure the title tag is unique and includes primary keywords towards the beginning.
- Craft meta descriptions like ad copy to boost click-through rates, incorporating focus keywords smoothly.
- Use the robots meta tag to adeptly manage crawler access, safeguarding against indexing of duplicate or irrelevant pages.
- Implement Open Graph and Twitter Card tags to facilitate richer social sharing experiences.
Best Practices for Using Meta Tags
- Keep title tags under 60 characters.
- Limit meta descriptions to 160 characters for optimal display.
- Regularly review and update meta tags to reflect content updates or keyword strategy shifts.
- Avoid generic descriptions; make each one unique and descriptive.
Case Studies on the Impact of Meta Tags
Numerous case studies demonstrate the value of optimized meta tags. For instance, businesses have seen significant upticks in organic traffic following revamps of their title tags and meta descriptions, solidifying the direct connection between well-executed meta tags and improved SERP positions.
Conclusion and Future of Meta Tags
While the digital marketing landscape is ever-evolving, the importance of meta tags remains constant. By mastering the art and science of meta tags, digital marketers and content creators can significantly influence both user experience and search engine rankings. These HTML elements might be invisible to the naked eye, but their impact on SEO and online visibility is profound. Incorporating the strategies outlined in this guide will ensure your content is not just seen but is also compelling enough to click.
Meta tags continue to be a foundational element of SEO optimization and digital marketing strategy. By staying informed and agile, marketers can leverage these tools to achieve remarkable success in the digital realm.

