Did you know that almost half of American adults suffer from periodontal disease? That means tens of millions of people are living with gum disease. So if you’re among them, know you’re not alone!
Periodontitis doesn’t just happen overnight. It’s a slow, progressive disease that worsens over time if left untreated. Because of this, there are a few gum disease stages to be aware of so you can remain vigilant of your oral health.
But what are these stages? And what are the signs of each? How does gum disease even happen?
If you find yourself asking questions such as these, wonder no longer because we’re here to help! In this article, we’ll give you all the information you need on periodontal disease to better protect yourself and your health.
Now then, let’s get started!
Causes of Gum Disease
First and foremost, the leading cause of gum disease is plaque. But there are a few other causes to keep in mind, such as the following.
Stress
A certain level of stress is simply unavoidable in life. In fact, there is even such a thing as good stress. But high amounts of stress and anxiety can have all kinds of negative effects on your body, including gum disease.
Smoking & Tobacco
Smokers have a higher risk of many diseases compared to non-smokers, but one of the most prevalent is gum disease. If you use tobacco products, you are four times more likely to develop periodontitis.
Diet
A healthy diet is key not only to your overall health, but your oral health as well. A deficiency in Vitamin C and calcium, two commonly under-consumed nutrients, can lead to gum disease, along with a myriad of other health problems. This dentist in Henderson also adds that iron deficiency can lead to gum diseases, especially in pregnant women.
Medication
Certain medications can affect your saliva production, which in turn can cause damage to your mouth. Saliva acts as a protective barrier for your teeth and gums. Without it, you are much more prone to disease.
Age
Now, your age isn’t necessarily correlated to your oral health. You can be young and have terrible oral health, or later in years and have a perfect smile. However, as we age, it’s common to slowly begin to neglect our health.
It’s important to remember that oral health, along with exercise and nutrition, are vital at every stage of life!
Gum Disease Stages
Gum disease doesn’t just happen overnight. It progresses slowly, through the following stages.
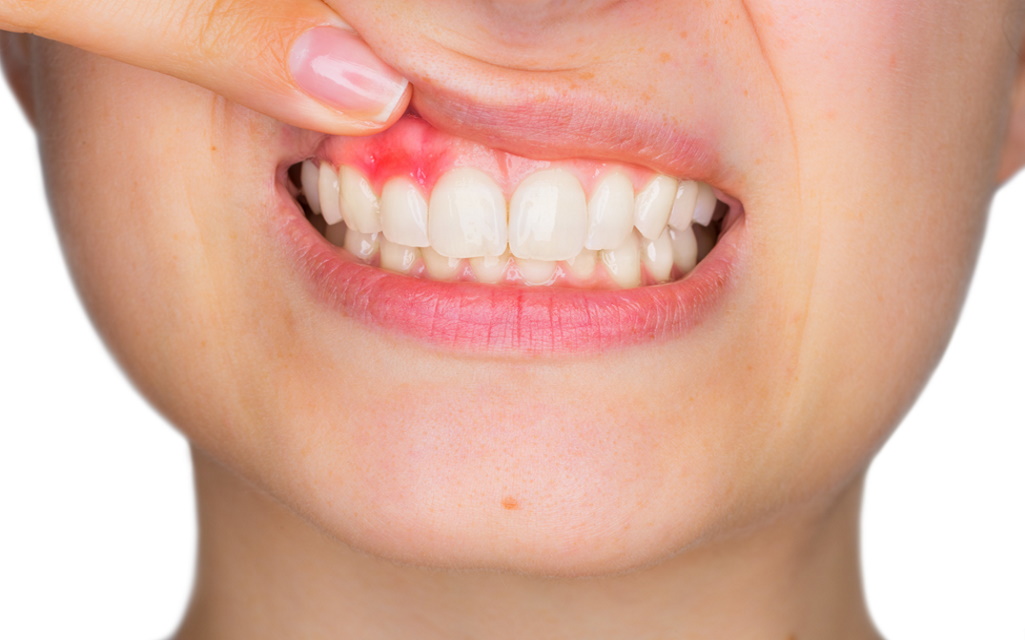
Stage I: Gingivitis
Gingivitis is inflammation of your gums and is the first stage of periodontal disease. This is caused by bacteria and plaque building up along your gums, which releases toxins that damage your teeth and soft tissue.
The symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Receding gum line
- Swelling of the gums
- Bleeding after flossing or brushing
- Discolored or tender gums
- Halitosis (bad breath)
If you recognize any of these symptoms in yourself, don’t panic! Gingivitis is completely reversible and can be corrected from your own home. There is no bone loss or tissue damage at this stage, so all you have to do is improve your oral health and you’re good to go.
Stage II-III: Mild to Moderate Periodontal Disease
Stages II and III of periodontal disease have similar signs. Stage III is simply a more advanced form of Stage II. At this point, the disease is no longer along the gum line, but deep in your actual gums.
In these stages, you will experience symptoms such as:
- Worsening receding of the gum line (4-5 mm with Stage II and 6-7 mm at Stage III)
- Increased bleeding when brushing and flossing
- More intense halitosis or bad breath
- Increased redness in your gums
- Bone loss between 20 and 50%
With Stages II and III, the infection is moving deeper into your gums, meaning that you will begin to see serious tissue damage. Additionally, if the infection gets deep enough, it will enter your bloodstream, opening the door for even more complications.
These stages cannot be treated at home and will require professional assistance to cure. Treatments such as a LANAP procedure can help to reverse the effects of the disease.
Stage IV: Advanced Periodontal Disease
In late-stage periodontal disease, you not only have an increased amount of bacteria, but the infection is at its most toxic.
The symptoms of advanced periodontal disease include:
- Extreme receding of the gums (>7 mm)
- Exposed roots of the teeth
- Loose and/or shifting teeth
- Bone loss between 50 and 90%
- Abscesses filled with pus around the gums